Introduction
For this part of my blog, I will discuss design patterns which were covered at University. Hopefully, I will be able through as many as possible in the forthcoming weeks. This is purely for my consolidation of knowledge and academic research for those who are reading.
So to start with...
What are software design patterns?
Well in software engineering we follow key principles in which makes the software work. These principles are design, development, maintenance, testing and evaluation of the software. Design patterns are a key part to developing robust solutions to common problems, what design patterns follow is simply a solution that is recognised within the industry of software development, that also improves understanding of software design as these designs are reusable, these solutions are considered a great way of solving problems within a given context of software design.
How are design patterns applied?
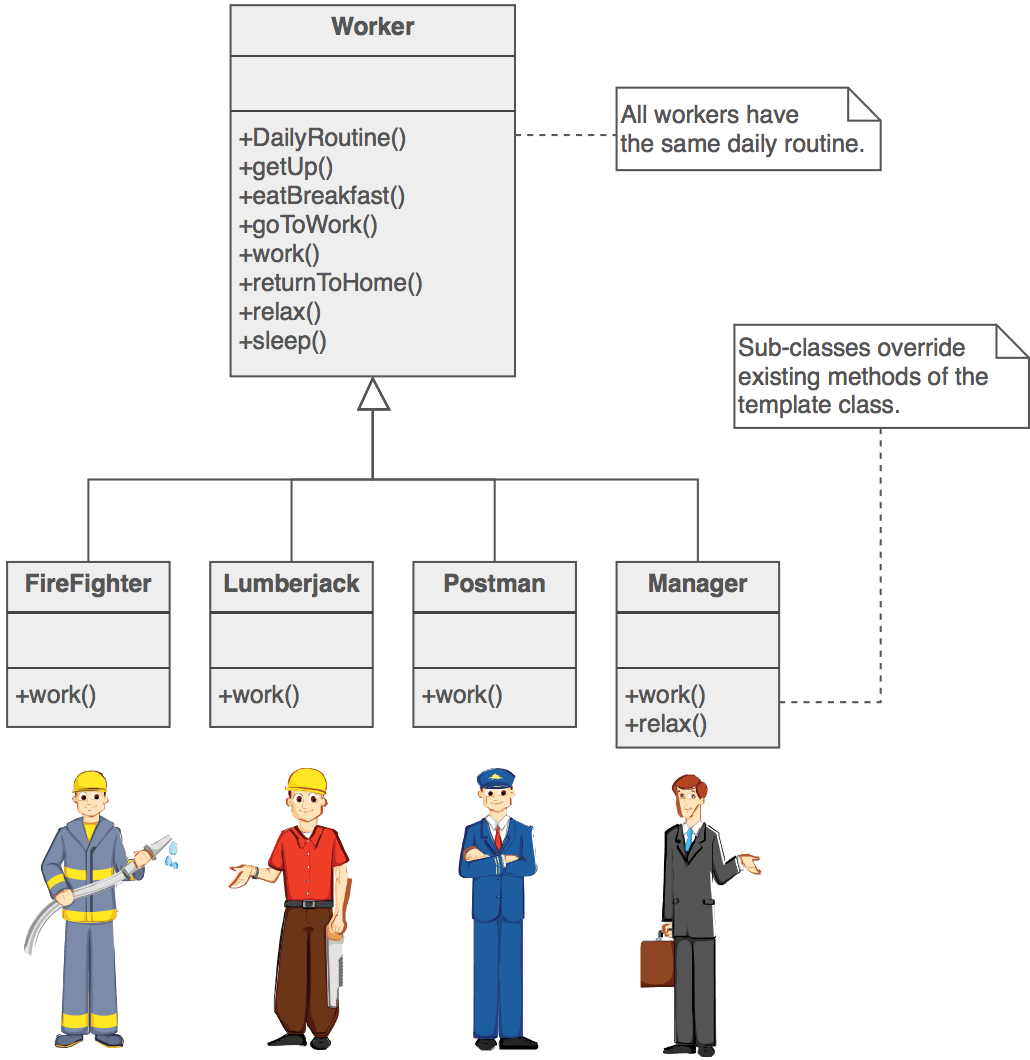
Often UML class diagrams are used to show the representation of the software design. What if we are using Object-Oriented design patterns as these diagrams will usually show relations and interactions between classes or objects that are involved.
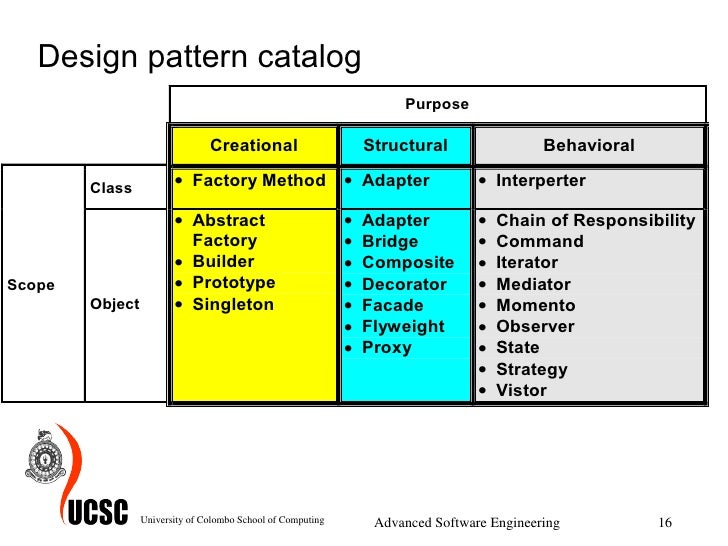
Below is an image of some of the different design patterns I will be covering.
https://image.slidesharecdn.com/patterns-msc-110923034042-phpapp02/95/design-patterns-16-728.jpg?cb=1316749339
Creational patterns: this focuses on object creation.
Behavioural patterns: this identifies common communication between objects and realises these patterns. By doing so, these patterns increase the potential flexibility in carrying out communication.
Structural patterns: this eases the design by identifying a simple way to realise the relationship between entities.
Concurrency patterns: this deals specifically with multi-threaded programming paradigm.
More to follow... Next will be looking at specific design patterns in detail






 https://www.codeproject.com/KB/Blogs/186192/1.jpg
https://www.codeproject.com/KB/Blogs/186192/1.jpg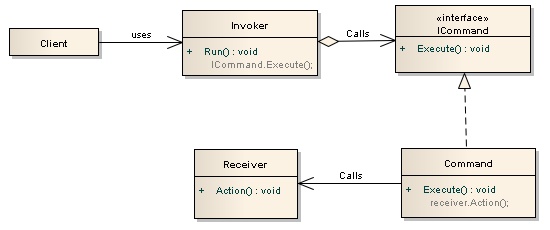 https://www.codeproject.com/KB/Blogs/186192/1.jpg
https://www.codeproject.com/KB/Blogs/186192/1.jpg